Leaving Community
Are you sure you want to leave this community? Leaving the community will revoke any permissions you have been granted in this community.
SAMPL5 is planned to include challenges based on aqueous host-guest binding data for three different host molecules, and on distribution coefficients of drug-like molecules partitioning between water and organic liquids.
Host-guest systems test simulation methods, force fields, and solvent models, in the context of binding, without posing the setup issues and computational burden of protein simulations.
The partition coefficients offer a particularly efficient test of force field accuracy when detailed simulations are used, and can also be used to test continuum solvation models and knowledge-based prediction methods.
Machine-readable structure files for the hosts, guests and solutes will be provided when the challenge opens.
Further information on the host-guest and partition coefficient parts of SAMPL5 is provided below.
We thank Dr. Lyle Isaacs (U. Maryland) and Dr. Bruce Gibb (Tulane U.) for providing host-guest challenge data, and Genentech for the partition coefficient data.
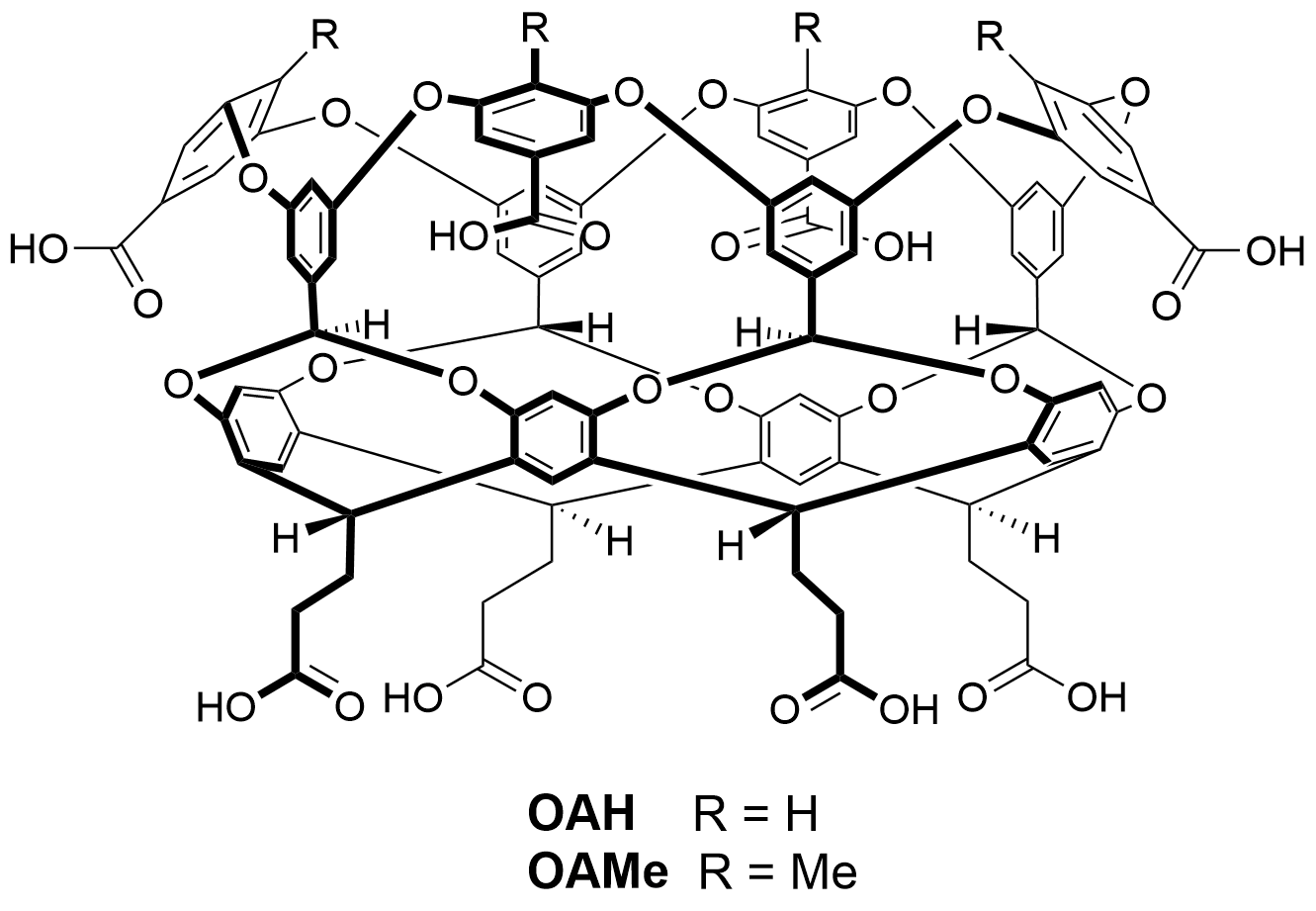
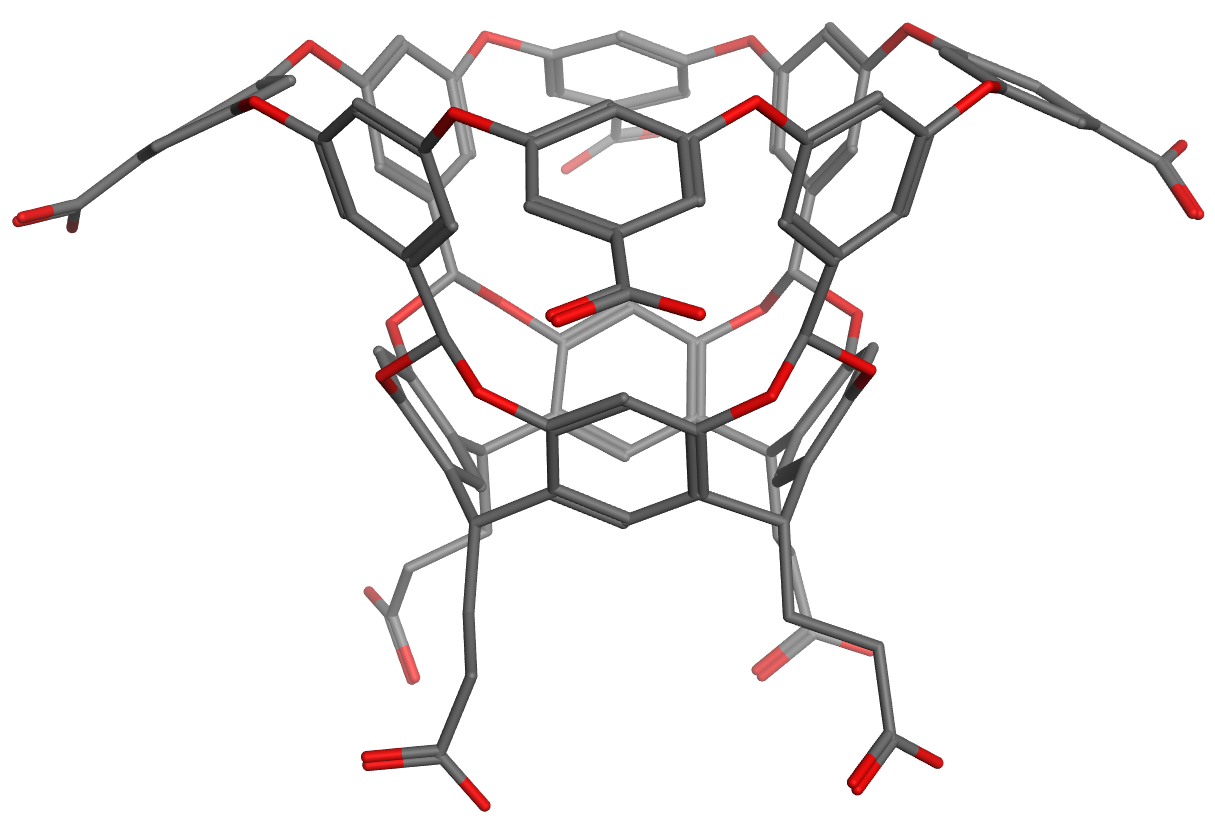
Host molecules OAMe and OAH
Host OAH is the octa-acid previously used in SAMPL4, and Host OAMe is the same except for the addition of four methyl groups, which alter the shape and depth of the hydrophobic cavity. Both were developed in the laboratory of Dr. Bruce Gibb (Tulane U), who will provide binding free energies and enthalpies, measured by ITC, for the same six guest molecules interacting with each host.
Host OAMe is described here: doi:10.1021/ja200633d; and Host OAH is described here doi:10.1007/s10822-013-9690-2. There are also a number of papers from SAMPL4 which discuss calculations for this system, as summarized here: doi:10.1007/s10822-014-9735-1.
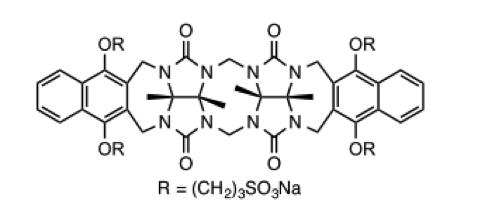
Host molecule CBClip
This host is a molecular “clip” related to the cucurbiturils used in SAMPL3 and SAMPL4. It was developed in the lab of Prof. Lyle Isaacs, who is measuring affinities for 10-15 guest molecules.
A paper describing this family of clips may be found here: doi:10.1039/c5ob00184f doi:10.1021/jm501276u. The clip which will be used in SAMPL5 is 2b (R = (CH2)3SO3Na) in this paper.
Distribution coefficients
Water-cyclohexane distribution coefficients have been measured at Genentech for 53 small, drug-like molecules. The technique used is a mass spectrometry-based assay as described in Lin & Pease, Combinatorial Chemistry & High Throughput Screening, 2013, 16, 817-825. Since no new hydration free energies are being measured and these distribution coefficients probe some of the same properties (namely, solvation in the respective solvents), we are excited about these as a replacement for hydration free energies in the SAMPL challenge. They also allow us to focus on larger, more drug-like molecules than have traditionally been part of the solvation component of SAMPL, and to include more functional group diversity.
This challenge was previously explained as involving partition coefficients, but technically, since the coefficients measured involve the relative concentrations of any form of the compound in the two phases, these are really distribution coefficients rather than partition coefficients.